Global warming is undeniable. Over the last 70 years, there have been unprecedented changes in our climate. Research shows that both the oceans and atmosphere have warmed, ice and snow have melted, and the sea level has risen.
What causes global warming?
Since the 1950s, greenhouse gas emissions have been the leading cause of global warming, induced by human activity. Greenhouse gases are gases that trap heat in the atmosphere and therefore increase the temperature over time. As outlined by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), greenhouse gases pose a problem beyond staying in the atmosphere – 60% end up stored in plants, soil and the ocean.
Greenhouse gases include:
- CO2 (carbon dioxide): generated, for example, through burning fossil fuels, trees (deforestation) and other materials (76%)
- Methane: generated through the production of coal, natural gas and oil, and livestock farming (16%)
- N2O (nitrous oxide): generated through industrial practices and agricultural practices (6%)
- Fluorinated gases: emitted during industrial processes (2%)
Greenhouse gas emission is also increasing over time. Around 50% of CO2 emissions occurred only in the last 40 years.
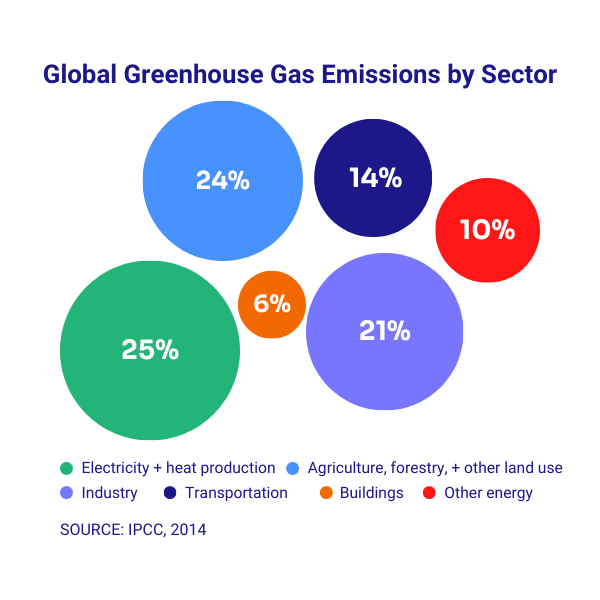
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the most significant economic sectors contributing to global greenhouse gas emissions and thus climate change are:
- Electricity and heat production (burning of coal, natural gas, and oil for electricity and heat),
- Agriculture, forestry and other land use (agriculture and deforestation)
- Industry (fossil fuels burned for energy, chemical, metallurgical, mineral transformation processes, and waste management activities)
What are the consequences of climate change?
The consequences are obvious: without any change to the current level of greenhouse gas emissions, global warming will only get worse. Besides temperature rising further, there will be long-lasting and irreversible changes to the ecosystems as well. Heat waves will last longer. Extreme events like droughts, floods, and wildfires will happen more frequently, and the ocean will continue to warm and acidify.
Many plants and animals will go extinct as they won’t be able to acclimate to changes caused by climate change fast enough. Marine animals will face lower oxygen, higher temperature and more acid environment, with coral reefs and polar ecosystems being the most vulnerable.
Global warming will affect most people through their food and water resources. Higher temperatures will impact food production levels as well as water resources. Another severe consequence people don’t often talk about is the impact on health. According to the WHO’s Health & Climate change report, the drivers of climate change contribute to 7 million deaths from air pollution annually. This means climate change is now the most significant health challenge of the 21st century.
What can our leaders do to save the Earth?
According to the IPCC’s recommendation, there are many mitigation options. Still, none of them are sufficient by itself, and the success depends on cooperation at all levels.
These options include changes in policies, innovation and investment into environmentally conscious technology and infrastructure and sustainable behavioral and lifestyle choices. IPCC also mapped out an approach to mitigate the risk:
- Vulnerability reduction: through education, poverty alleviation, ecosystem management (maintenance of green spaces and genetic diversity), etc.
- Adaptation: through power plant and electricity grid adjustments, ecological restoration, public health services and economical options like financial incentives, etc.
- Transformation: through a change in agricultural practices, social innovations and political decisions consistent with reducing risk, etc.
Given that the US is responsible for 15% of all global emissions and is the second-largest contributor after China, it has a special responsibility to participate in mitigating the crisis.
But what can we do to save the Earth?
The GEO-6 report (Global Environment Outlook) arrived at similar conclusions at the individual level. To be able to deal with human-induced damages, we need to transform our way of life. This includes consumption, production, lifestyles and even people’s understanding of “sustainability”.
In our Save the Earth Series, we will deep dive into the main contributors to climate change and how we can stand against it individually.



